Solaris:Logical Domains
Introduction to a Virtual Network
A virtual network allows domains to communicate with each other without using any external physical networks. A virtual network also can allow domains to use the same physical network interface to access a physical network and communicate with remote systems. A virtual network is created by having a virtual switch to which you can connect virtual network devices.
Virtual Network Device
A virtual network (vnet) device is a virtual device that is defined in a domain connected to a virtual switch. A virtual network device is managed by the virtual network driver, and it is connected to a virtual network through the hypervisor using logical domain channels (LDCs).
A virtual network device can be used as a network interface with the name vnetn, which can be used like any regular network interface and configured with the ifconfig(1M) command.
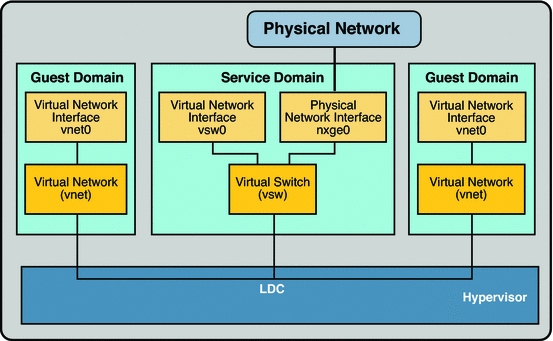
Following is a explanation for the example in the figure.
- The virtual switch in the service domain is connected to the guest domains. This allows guest domains to communicate with each other.
- The virtual switch is also connected to the physical network interface nxge0. This allows guest domains to communicate with the physical network.
- The virtual switch network interface vsw0 is plumbed in the service domain, so this allows the two guest domains to communicate with the service domain.
- The virtual switch network interface vsw0 in the service domain can be configured using the ifconfig(1M) command.
- The virtual network interfaces vnet0 in the guest domains can be configured using the ifconfig(1M) command.
Basically the virtual switch behaves like a regular physical network switch and switches network packets between the different systems, such as guest domains, service domain, and physical network, to which it is connected.