Unix:HP StorageWorks Continuous Access: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (moved HP StorageWorks Continuous Access to Unix:HP StorageWorks Continuous Access: Move to Unix Name Space.) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:HP]] | |||
[[Category:Unix]] | |||
===Volume pairs=== | ===Volume pairs=== | ||
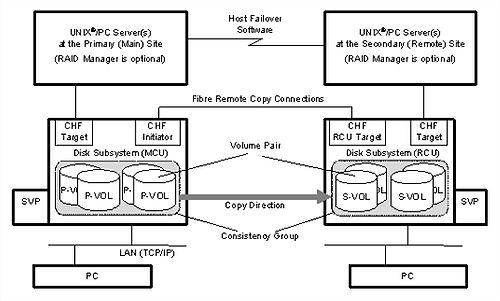
[[File:HP StorageWorks P9000 Continuous Access Synchronous User Guide - Continuous Access Synchronous Components.jpg|Continuous Access Synchronous Components|right|border|500px]] | [[File:HP StorageWorks P9000 Continuous Access Synchronous User Guide - Continuous Access Synchronous Components.jpg|Continuous Access Synchronous Components|right|border|500px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:14, 1 November 2010
Volume pairs
As described above, original data is stored in the P-VOL and the remote copy is stored in the S-VOL. The pair can be split, resynchronized, reverse resynchronized, and returned to the SMPL state.
- When paired, the volumes are synchronized.
- When split, new data is sent to the P-VOL but not the S-VOL.
- When re-synchronized, changed data is copied to the S-VOL.
- When necessary, data in the S-VOL can be copied to the P-VOL.
During normal operations, the P-VOL remains available to the host for read and write I/O operations. The secondary system rejects write I/Os for the S-VOL, unless the write-enable option is specified for P9000 Continuous Access Synchronous User Guide 13 the S-VOL. Then, write I/O is allowed to the S-VOL while the pair is split. In this instance, S-VOL and P-VOL track maps keep track of differential data and are used to re-synchronize the pair. Logical units on the local and remote systems must be defined and formatted prior to pairing.
Data path
Continuous Access Synchronous operations are carried out between local and remote systems connected by a fibre channel interface. The data path, also referred to as the remote copy connection, connects ports on the local P9500 system to the ports on the remote system. The ports are assigned attributes that allow them to send and receive data. One data path connection is required, but two or more independent connections are recommended, for hardware redundancy. A maximum of eight paths per control unit (CU) can be used.
Consistency groups
A consistency group is a set of volume pairs that are in the same primary and secondary systems, on which copy operations are performed simultaneously, and in which the pairs’ status remains consistent. When you issue a command, it is executed on all pairs in the group. The pairs’ pair status changes at the same time, depending on group options. Yet, while consistency is a primary function of a group, certain operations take priority. For example, if the PSUS command is issued to a consistency group in which one of the pairs is in the process of being updated, the pair is not PSUS immediately, as all the other pairs are. It is PSUS only when the update operation is completed. This allows for data integrity to be maintained between P-VOLs and S-VOLs. The same behavior occurs for a suspend operation caused by system failure. Continuous Access Synchronous operations can be performed on pairs in a maximum of 128 consistency groups on the primary system.
Interfaces
You perform Continuous Access Synchronous operations using of the following interfaces:
- Remote Web Console, a browser-based interface from which Continuous Access Synchronous can be setup, operated, and monitored. The GUI provides the simplest method for performing operations, requiring no previous experience.
- The primary system must be LAN-attached to a Remote Web Console computer.
- The secondary system should also be LAN-attached to a separate Remote Web Console at the remote site. This allows you to perform operations more efficiently on the secondary system in the event that the main site is not available.
- RAID Manager is a command line interface used to display pair information and perform all copying and pair-managing operations. RAID Manager provides a full scripting capability which can be used to automate replication operations. RAID Manager is required for performing failover operations.
Failover software
Host failover software is used to transfer information between host servers at the local and remotesites. It is a critical component of any disaster recovery solution.
- When Continuous Access Synchronous is used as a disaster recovery tool, host failover is required to insure effective recovery operations.
- When Continuous Access Synchronous is used as a data migration tool, host failover is recommended. Continuous Access Synchronous does not provide host-failover functions. Use the failover software most suitable for your platform and requirements (for example, Microsoft Cluster Server).
- MCA Main Control Unit
- RCA Remote Control Unit
- SVP Service Processor
- P-VOL Primary Volume
- S-Vol Secondary Volume